Jamstack is a modern web architecture that separates the frontend from the backend, relying on static site generation, APIs, and CDN delivery to achieve exceptional speed, security, and scalability. Instead of rendering pages on every request, Jamstack pre-builds pages and serves them globally, resulting in lightning-fast performance and improved SEO.
In today’s web landscape, users expect lightning-fast load times, rock-solid security, and seamless scalability. Traditional monolithic architectures often struggle to keep up with these demands. Enter Jamstack—a modern web development architecture that decouples the frontend from the backend, harnesses the power of static site generation, headless content management, and global content delivery networks (CDNs). This guide dives deep into the world of Jamstack, exploring its core components, benefits, step-by-step setup, and best practices to help you build enterprise-grade, high-performance websites.
What Is Jamstack?
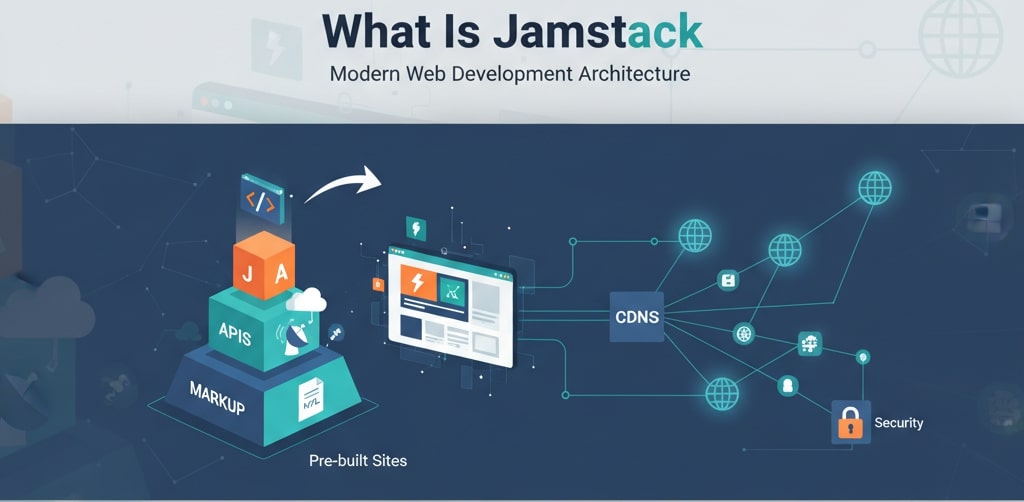
Jamstack stands for JavaScript, APIs, and Markup. Rather than rendering pages on the server per request, Jamstack sites generate static HTML at build time. Dynamic functionality is achieved through client-side JavaScript and reusable APIs. By shifting rendering to the build process and serving pre-built markup from a CDN, Jamstack delivers unmatched speed, reliability, and security.
Jamstack vs Traditional Web Architecture
Traditional web architectures rely heavily on server-side rendering, databases, and tightly coupled backend logic. Every visitor request triggers a chain reaction—database queries, template rendering, authentication checks—which can slow down performance and increase vulnerability.
Jamstack flips this model by decoupling the frontend from the backend and delivering pre-built static assets directly through a CDN. Instead of generating pages on request, Jamstack compiles everything during the build phase, drastically reducing runtime processing. This separation leads to faster load times, fewer bottlenecks, and a more maintainable codebase. While traditional stacks demand ongoing patching, scaling strategies, and complex server management, Jamstack minimizes infrastructure overhead and maximizes developer productivity. This architectural difference is what makes Jamstack especially attractive for modern, high-traffic platforms that require global reach, strong security, and continuous iteration.
How Jamstack Enhances Developer Workflow
Jamstack introduces a development workflow that aligns perfectly with modern engineering practices. By using Git-centric deployments, developers push code to a repository and trigger automated builds and previews. This tight integration between Git, CI/CD pipelines, and hosting platforms helps teams move faster with fewer deployment risks.
Developers benefit from decoupled systems—frontend teams can work independently from content teams, and backend logic can be modularized through serverless APIs. Hot reloading, component-driven frameworks, and automated previews improve collaboration while reducing context switching. Most importantly, Jamstack supports atomic deployments: every build is immutable and versioned, ensuring that users always receive consistent, error-free pages. This workflow empowers rapid experimentation without fear of breaking production, making Jamstack ideal for iterative development, A/B testing, and agile product teams.
Jamstack for Enterprise and Large-Scale Projects
Large organizations often prioritize security, regulatory compliance, reliability, and scalability. Jamstack directly aligns with these requirements. Enterprises can use pre-rendered pages served via global CDNs to guarantee low-latency performance worldwide, reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure. Because Jamstack minimizes server exposure, it significantly reduces the attack surface—an important factor for industries like finance, healthcare, and SaaS.
Enterprises also benefit from modular integrations. Instead of being locked into a monolithic CMS or backend, Jamstack allows teams to mix and match specialized API services—authentication, search, payments, analytics, personalization. This “best-of-breed” approach ensures long-term flexibility and reduces vendor lock-in. Combined with incremental builds, role-based CMS access, and edge functions, Jamstack empowers large teams to maintain performance at scale, improve reliability, and modernise ageing digital platforms without complete rewrites.
Jamstack for SEO and Core Web Vitals

Search engines reward fast, well-structured, accessible websites—and Jamstack naturally aligns with these ranking factors. Because Jamstack sites ship pre-built HTML and optimised assets from CDNs, they achieve exceptional performance across First Contentful Paint (FCP), Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), and Time to Interactive (TTI). Search crawlers can easily index pre-rendered pages without relying on heavy JavaScript or client-side rendering.
Developers can also generate metadata, structured schema, sitemaps, and robots files during build time to ensure complete and consistent SEO optimization. Serverless functions and edge logic allow for user-based personalization without compromising indexability. With Google’s increasing emphasis on Core Web Vitals, Jamstack architecture gives websites a competitive advantage by combining speed, cleanliness of code, and predictable rendering behavior.
Jamstack and the Future of Web Development
Jamstack is more than a trend—it’s a foundational shift toward distributed, API-driven digital experiences. As businesses adopt omnichannel strategies and decoupled architectures, Jamstack becomes a natural evolution. The rise of AI-driven content workflows, smart caching, and real-time edge rendering will push Jamstack even further into mainstream adoption.
We’re already seeing SSGs evolve into hybrid frameworks that support static generation, SSR, and on-demand rendering. Edge functions bring logic closer to users, enabling hyper-personalized experiences without sacrificing speed. The future of Jamstack lies in this blend of static reliability and dynamic intelligence—allowing developers to build experiences once considered impossible with traditional static sites. Jamstack is shaping the next generation of performant, modular, and scalable digital ecosystems.
Common Challenges and How to Solve Them
While Jamstack offers impressive advantages, it also introduces unique challenges. One of the most common issues is long build times for content-heavy websites. This can be solved with incremental builds, selective content regeneration, and distributed build pipelines. Another challenge is handling dynamic features like authentication, search, and complex user dashboards—these require serverless functions, third-party APIs, or client-side rendering strategies.
Content editors may also struggle with previewing content changes. To fix this, teams can integrate on-demand preview environments provided by CMS platforms or custom preview endpoints. Additionally, managing multiple third-party services can become overwhelming, but using an orchestration layer or a DX-focused platform like Vercel or Netlify helps centralize configurations. With proper planning and tooling, these challenges are easily manageable and rarely outweigh Jamstack’s benefits.
Real-World Use Cases of Jamstack
Jamstack is versatile and supports a wide range of projects across industries. E-commerce brands use Jamstack to deliver lightning-fast headless storefronts that boost conversions and reduce cart abandonment. Publishing companies rely on its scalability to handle massive spikes in traffic without downtime. Tech companies and SaaS platforms adopt Jamstack for documentation hubs, marketing sites, and developer portals—ensuring reliable, versioned deployments.
Nonprofits and educational institutions appreciate its affordability and security, while enterprises integrate Jamstack into complex ecosystems that span web apps, mobile experiences, and IoT platforms. From personal blogs to Fortune 500 websites, Jamstack offers a flexible foundation that adapts to almost any digital requirement. These diverse use cases highlight why Jamstack is rapidly becoming a standard architecture across modern web development.
Core Components of a Jamstack Architecture
A typical Jamstack project relies on three pillars:
- Static Site Generators (SSGs): Tools like Gatsby, Next.js (in static export mode), Hugo, and Eleventy compile content and templates into static HTML files during build time.
- Headless CMS and APIs: Services such as Contentful, Strapi, Sanity, or even Git-based solutions (Netlify CMS, Forestry) store and manage content. Your frontend fetches data via REST or GraphQL APIs.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Platforms like Netlify, Vercel, Cloudflare, and Fastly deploy and distribute your static assets across a global network, ensuring minimal latency and maximum uptime.
Key Benefits of Jamstack

1. Unmatched Performance
By serving pre-rendered HTML directly from a CDN, Jamstack pages load in milliseconds. There’s no need to wait for database queries or server-side rendering on each request, resulting in a consistently fast user experience and better Core Web Vitals scores.
2. Enhanced Security
With no direct connection to a server-side application or database at runtime, attack surfaces shrink dramatically. Static files can’t be exploited by SQL injection or server-side vulnerabilities, and any dynamic operations occur through hardened, third-party APIs.
3. Seamless Scalability
Scaling a Jamstack site is as easy as caching and distributing static assets on a CDN. Whether you’re serving a handful or millions of visitors, CDNs handle the load without requiring infrastructure changes or complex auto-scaling configurations.
Building Your First Jamstack Site: Step-by-Step
Follow these steps to create a Jamstack-powered website from scratch:
Step 1: Choose a Static Site Generator
Select the SSG that fits your project requirements and preferred stack. For React developers, Next.js or Gatsby are popular choices. If you favor speed and simplicity, Hugo or Eleventy may be ideal.
Step 2: Set Up Your Project
Use the SSG’s CLI to scaffold a new site. For example, to create a Next.js site, run npx create-next-app my-jamstack-site. Install any additional plugins, themes, or CLI tools needed for your workflow.
Step 3: Integrate a Headless CMS
Choose a headless CMS based on content needs and budget. Configure content models (e.g., pages, blog posts, authors) and set up API credentials. In your frontend code, fetch content at build time using REST or GraphQL calls to the CMS.
Step 4: Add Dynamic Functionality
Use JavaScript to power interactive features like search, forms, or e-commerce. Consider serverless functions (AWS Lambda, Netlify Functions, Vercel Serverless Functions) to handle form submissions, authentication, or custom API endpoints securely.
Step 5: Configure Deployment and CDN
Connect your Git repository to a Jamstack-friendly hosting service (Netlify, Vercel, Cloudflare Pages). Configure build settings and environment variables. The platform will automatically build your site on each push and deploy static assets globally.
Step 6: Optimize for SEO and Accessibility
Generate sitemap.xml, robots.txt, and metadata (title, description, Open Graph tags) at build time. Ensure semantic HTML, alt attributes on images, and proper heading structure for screen readers. Leverage prerendered pages and CDN edge caching to improve SEO crawlability.
Jamstack Best Practices
- Incremental Builds: Use SSGs or hosting platforms that support partial or incremental builds to update only changed pages, speeding up build times for large sites.
- Image Optimization: Integrate image processing libraries (Sharp, Imgix) or cloud-based image services to resize and serve images in modern formats (WebP, AVIF).
- Edge Functions: Offload geolocation, A/B testing, or personalization logic to edge functions for lower latency and better user experience.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Implement real user monitoring (RUM), log forwarding, and lightweight analytics (Plausible, Fathom, or serverless Google Analytics) to gain insights without slowing down pages.
- Accessibility Compliance: Follow WCAG guidelines, use automated testing tools (Axe, Lighthouse), and conduct manual audits to ensure your site is usable by all audiences.
Popular Jamstack Tools and Platforms

Here are some industry-leading tools to power your Jamstack projects:
- Static Site Generators: Next.js, Gatsby, Hugo, Eleventy
- Headless CMS: Contentful, Strapi, Sanity, Netlify CMS
- Hosting & CDN: Netlify, Vercel, Cloudflare Pages, AWS Amplify
- Serverless Functions: AWS Lambda, Netlify Functions, Vercel Serverless Functions
- Image Optimisation: Imgix, Cloudinary, Sharp
Conclusion
Jamstack represents a paradigm shift in web development, prioritising speed, security, and scalability by decoupling the frontend from traditional server-side architectures. By leveraging static site generators, headless CMS platforms, and global CDNs, you can build robust websites that delight users and simplify maintenance. Whether you’re launching a marketing site, blog, or e-commerce store, adopting Jamstack will future-proof your projects and deliver exceptional performance. Ready to get started? Pick your favourite tools, follow the steps outlined above, and join the growing community of Jamstack developers reshaping the web.
FAQ: Jamstack Architecture
1. Is Jamstack only for static websites?
No. While Jamstack relies on pre-rendered static HTML, it fully supports dynamic features through APIs, client-side JavaScript, and serverless functions—making it suitable for blogs, e-commerce, SaaS dashboards, and even enterprise apps.
2. Does Jamstack improve SEO?
Yes. Jamstack sites load extremely fast due to CDN delivery and pre-rendered HTML, which boosts Core Web Vitals and overall SEO. Proper metadata, sitemap generation, and accessibility further enhance search performance.
3. Is a headless CMS required for Jamstack?
No, but it’s highly recommended. You can use markdown files or Git-based CMSs, but headless CMS platforms (Contentful, Sanity, Strapi, etc.) provide better scalability, workflows, and content modelling for larger or dynamic sites.
4. Can Jamstack handle e-commerce functionality?
Absolutely. Jamstack integrates seamlessly with API-based commerce solutions like Shopify Headless, Snipcart, BigCommerce, and Commerce.js, enabling secure, fast, and scalable e-commerce websites.
5. Is Jamstack suitable for enterprise-level projects?
Yes. Enterprises adopt Jamstack for improved performance, security, and scalability. With incremental builds, serverless functions, and edge networks, it supports large-scale projects with complex workflows.
6. Do I need to know advanced JavaScript to build Jamstack sites?
Basic JavaScript is enough for simpler sites, but dynamic features (search, auth, e-commerce, serverless functions) require intermediate to advanced skills. Tools like Next.js simplify much of the process.
7. Are Jamstack sites cheaper to host?
Usually, yes. Static hosting on CDNs (Netlify, Vercel, Cloudflare Pages) is often free or low-cost. There’s no need for traditional servers or database hosting, which reduces infrastructure expenses.
8. How often does a Jamstack site rebuild?
Whenever you publish new content or push code. Many platforms also support incremental or on-demand builds to improve performance on large sites.
9. Can Jamstack work with WordPress?
Yes. WordPress can be used in headless mode via its REST or GraphQL APIs. You keep the familiar WP dashboard while using React, Next.js, or Gatsby to build a fast Jamstack frontend.